Differences Between Sunburn, Sun Poisoning, Heat Rash, Heat Exhaustion

| 2 min read
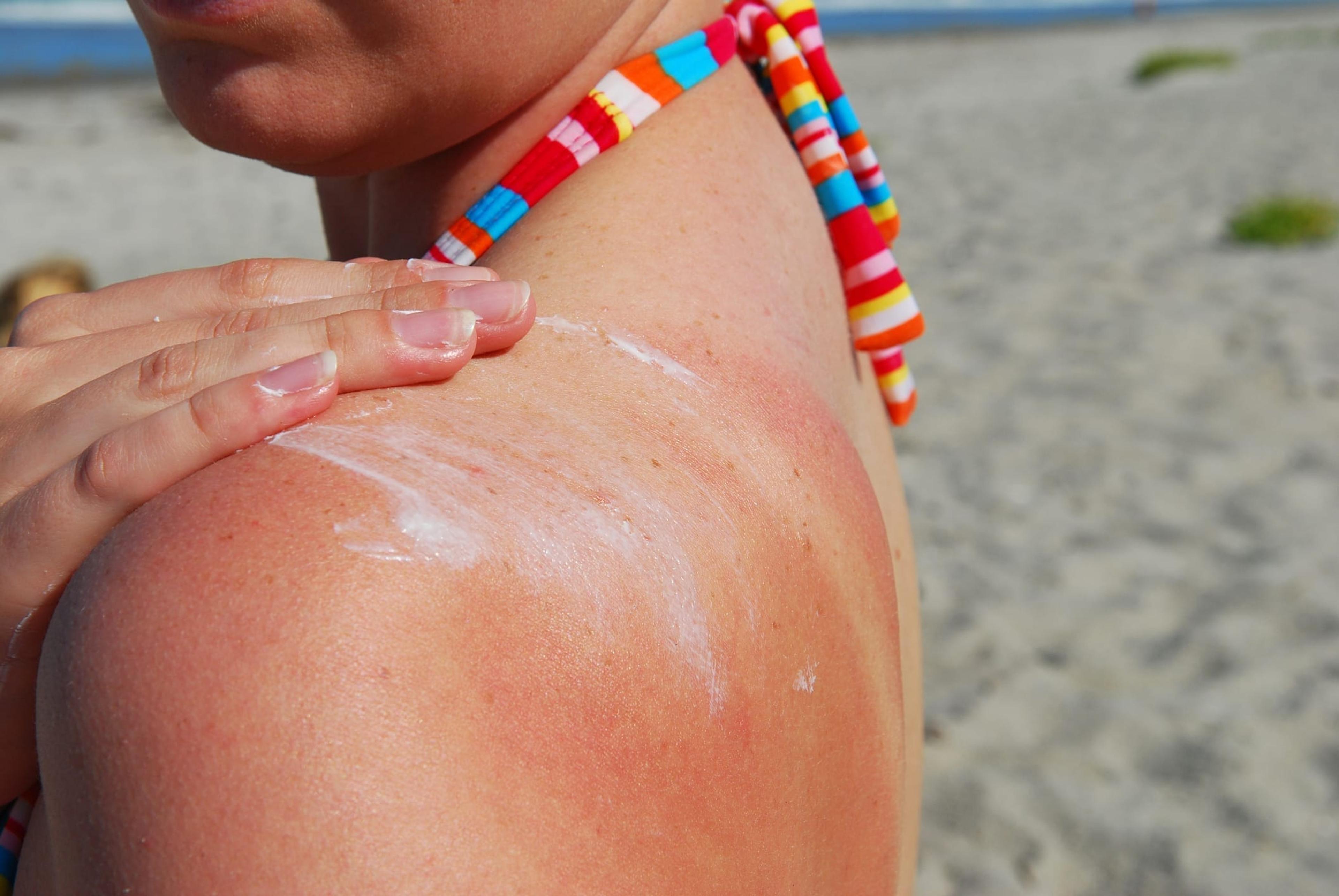
- Sunburn: A major sign of overexposure to UV rays is sunburn. It can range from mild to severe and is characterized by redness, tenderness and in some cases, blisters. Pain can last between 6 and 48 hours and can cause permanent damage. To treat sunburn, briefly apply cool water, a cold compress or ice to the affected area. Moisturize skin with a non-petroleum or oil-based lotion. You may also take a pain reliver such as naproxen or ibuprofen.
- Sun Poisoning: Sun poisoning is an extreme case of sunburn that can cause internal and external symptoms. Aside from blistering skin, a person may experience headaches, nausea, dehydration and dizziness. Sun poisoning can last for days or even weeks depending on the amount of exposure. A doctor may treat the condition with a cold compress, oral steroids, lotions, or topical antibiotics.
- Heat Rash: In hot or humid weather, the skin’s pores can become clogged with sweat. When this occurs, perspiration is trapped causing an eruption on the surface called heat rash. It can develop in high-friction areas like underarms, elbow creases, and inner thighs. Heat rash can be treated with over-the-counter remedies such as calamine lotion, aloe vera, and ointment.
- Heat Exhaustion: This condition is caused by heavy sweating and a loss of water and vital electrolytes. A person becomes dehydrated and the body can no longer regulate its temperature. Noticeable symptoms include lightheadedness, thirst, increased heart rate, weakness, shallow breathing, and a reddish face. Individuals should immediately find a cool, shaded area and rehydrate. They should also cover their face with a cold, wet cloth or take a cool shower.

- Skin Cancer: Start Protecting Yourself Today
- Why Regular Skin Screenings Matter
- How to Stay Safe During a Socially Distant Summer





